Symptoms and Transmission: Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
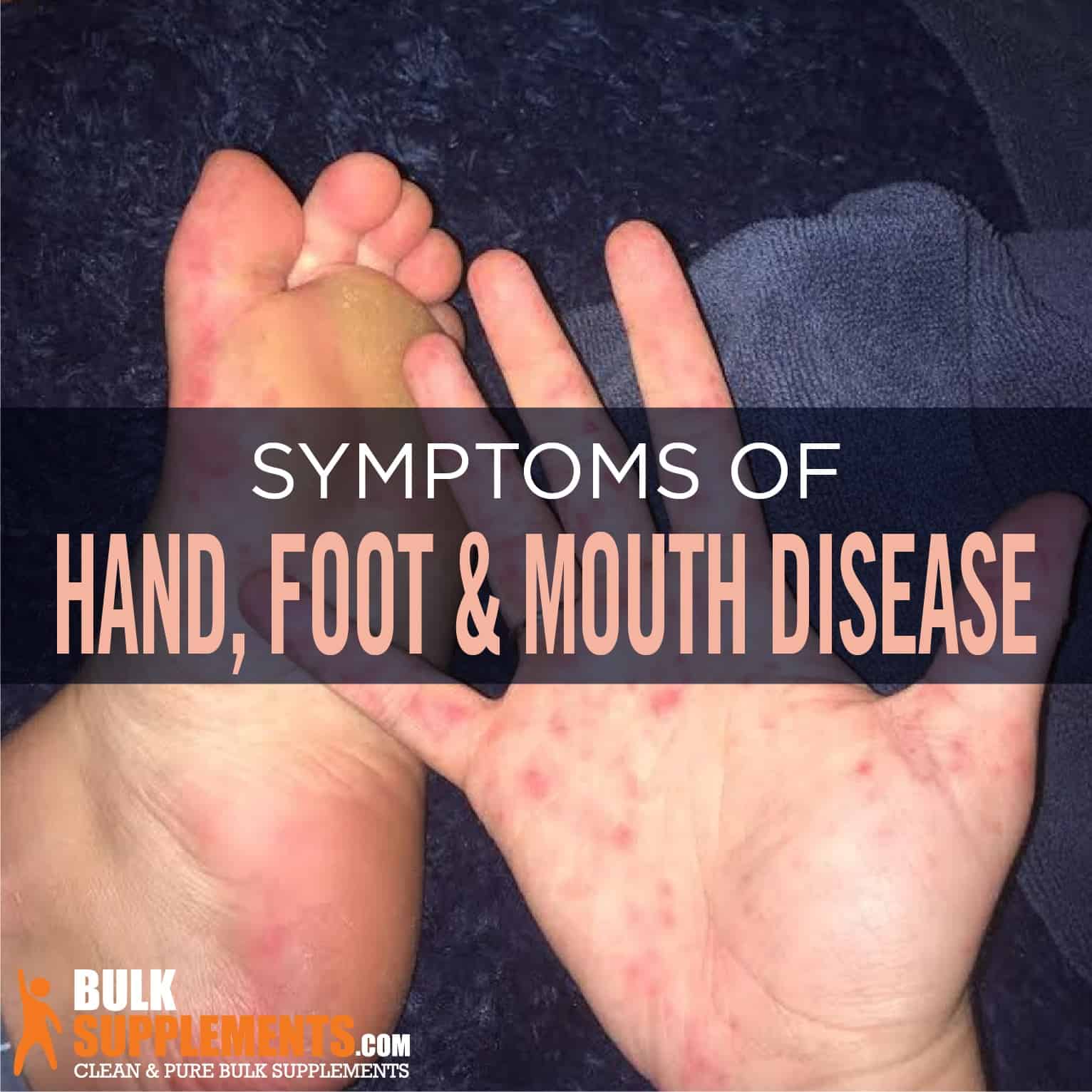
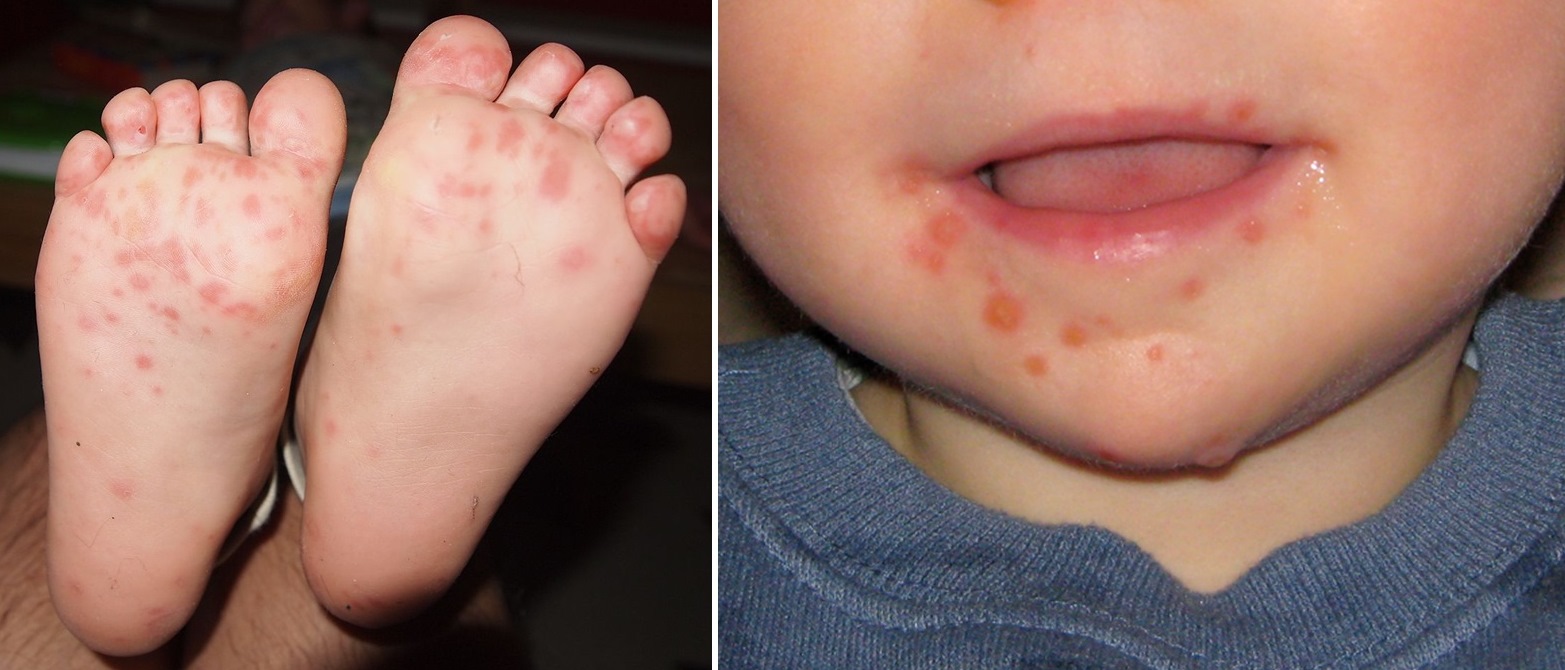
Hand foot and mouth disease – Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood illness that is caused by a virus. The virus is spread through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or feces. Symptoms of HFMD include fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common childhood illness, can cause fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth. The virus that causes the disease can be spread through contact with infected people or objects. While there is no specific treatment for the disease, most people recover within a few days.
However, in rare cases, the virus can cause serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis. The Minnesota Vikings football team has been affected by the disease in the past, with several players contracting the virus during the 2019 season. The team took steps to prevent the spread of the virus, including isolating infected players and disinfecting the team’s facilities.
The incubation period for HFMD is typically 3-7 days. The illness usually lasts for 7-10 days. Most people who get HFMD recover completely, but some people may develop complications such as meningitis or encephalitis.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common childhood illness caused by a virus. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth. The virus can spread through contact with infected saliva or feces. There is no specific treatment for hand, foot, and mouth disease, but symptoms usually resolve within a few days.
Davante Adams vs Chargers is a matchup to watch in the NFL this week. Adams is one of the best receivers in the league, and he will be facing off against a tough Chargers defense. It should be a great game.
Transmission
HFMD is spread through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or feces. The virus can be spread through coughing, sneezing, or sharing food or drinks. It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as toys or doorknobs.
Who is Most at Risk?
Children under the age of 5 are most at risk for HFMD. However, anyone can get the illness. People who are in close contact with children, such as parents, teachers, and daycare workers, are also at increased risk.
Treatment and Prevention
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is typically a mild and self-limited illness that resolves within a few days to a week. However, there is no specific treatment for the disease.
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be used to reduce fever and discomfort. Gargling with warm salt water can help soothe sore throats. Adequate hydration is essential to prevent dehydration.
Prevention
Prevention of hand, foot, and mouth disease is primarily based on good hygiene practices. Frequent hand washing with soap and water, especially after using the toilet, changing diapers, or coming into contact with an infected person, is crucial.
Avoiding close contact with infected individuals, sharing personal items, or touching contaminated surfaces can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Vaccination, Hand foot and mouth disease
A vaccine against hand, foot, and mouth disease is available in some countries. The vaccine is recommended for children between 6 months and 5 years of age. It is not 100% effective, but it can help reduce the severity of symptoms and prevent complications.
Complications and Outlook
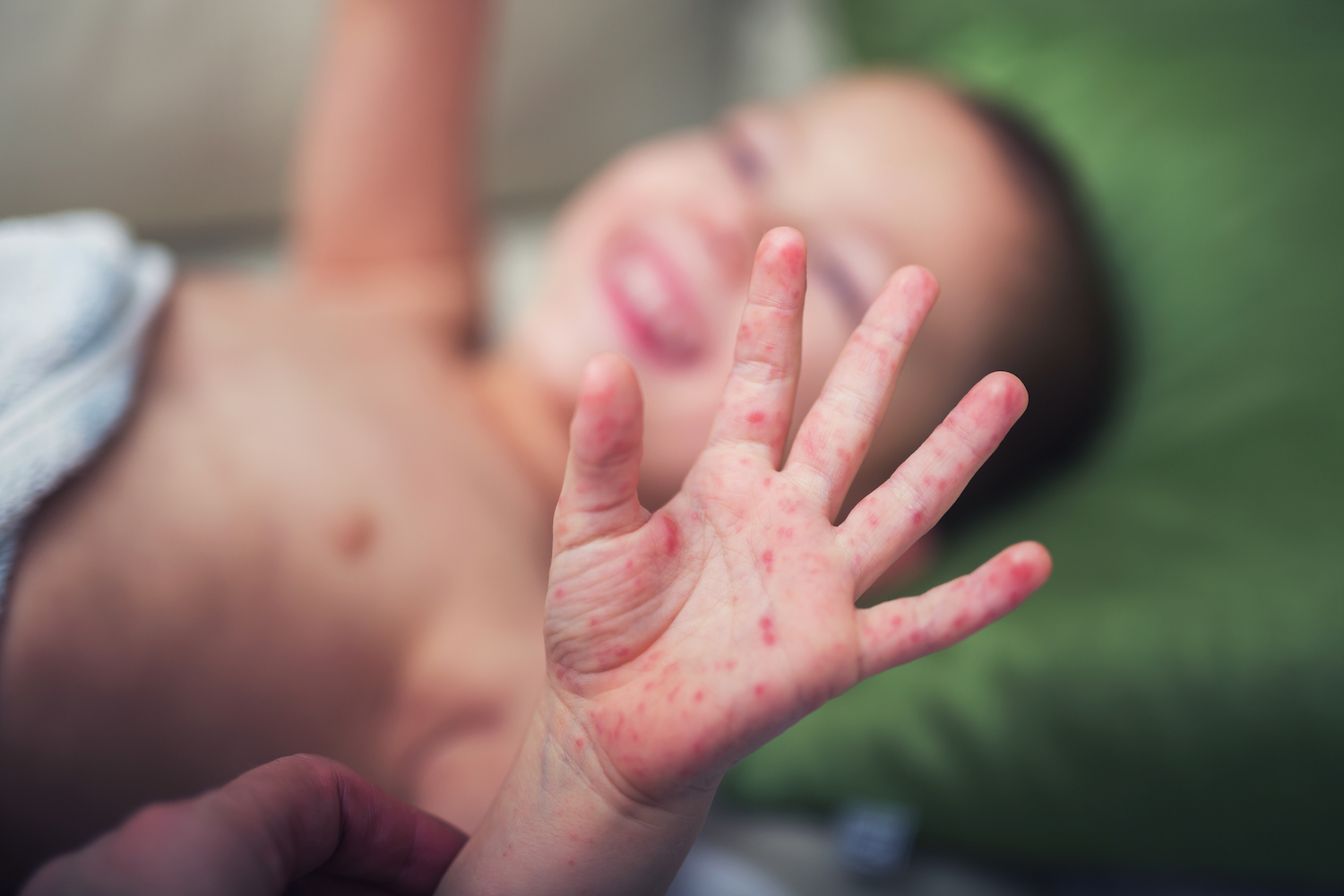

Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) usually resolves within a week or two without complications. However, in rare cases, it can lead to more severe problems, such as:
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord.
- Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain.
- Paralysis: Weakness or loss of movement in the arms, legs, or face.
These complications are more likely to occur in young children, especially those under the age of 5. They can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Prognosis
Most people with HFMD recover fully within a few weeks. However, in some cases, the virus can cause long-term effects, such as:
- Nail loss: The nails may become discolored, brittle, and fall off.
- Skin problems: The skin may become dry, itchy, and cracked.
- Dental problems: The teeth may become discolored or develop cavities.
These long-term effects are usually mild and will eventually go away. However, they can be a nuisance and may require treatment.
Follow-up Care
Most people with HFMD do not need to see a doctor. However, it is important to seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
- A fever that lasts more than 24 hours
- A headache that is severe or does not go away
- Stiff neck
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Rash that is spreading or becoming more painful
If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor right away. They will be able to diagnose HFMD and recommend the best course of treatment.